
Hi friends! A large part of costume design is research. Fashion has been around since the invention of clothes with what is happening in the world effecting what is fashionable. In other words, as society evolves and history unravels, so does fashion. As a costumer, it important to have a basic knowledge of fashion history and to use responsible sources in your further research. One of my favorite courses in college was fashion history. Its the perfect mix of what I love–fashion and history. No duh. As an ongoing assignment throughout the semester, we needed to create our own fashion history bible. This is a binder that covers basics facts, events and fashion starting from ancient civilizations to modern day as well as some renderings of people in period clothing. Today I’ve decided to share with you what’s in my binder for the Ancient Middle East.
The Ancient Middle East
3500-600 BCE
During this time, the civilizations of Mesopotamia and Egypt dominated this area. In ancient Mesopotamia, occupying area from the Persian Gulf to near the borders of modern Iraq and Turkey, cities started popping up in the southern parts of the region by the rivers. There were rich, fertile plains which created a good agricultural and herding civilization. The Sumerians founded the first cities in 3500 BCE and invented a form of writing. They remained a system of city states with no strong government. They were conquered by the Akkadiens who were then conquered by the Amorites who established a capital in Babylon. King Hammurbi is known for his law code dealing with almost every aspect of life. Babylonian power declined about 1700 BCE as they were attacked by a series of invaders. Around 1000 BCE the Assyrians from the upper Tigris River conquered them. The Assyrians had a large empire, were cruel, and were hated for it. They were conquered by the Chaldeans in 612 BCE who were in turn conquered by the Persians in 539 BCE under Cyrus. Chaldean Babylon was known for its luxury and wealth and work in astronomy.
Egypt is more separated from the rest of the world, because it has a natural barrier of the sea and the desert. Agriculture flourished thanks to the annual flooding of the Nile River. Ancient Egypt flourished under the Greeks led by Alexander the Great who conquered Egypt. The history is divided into six periods: The Early Dynastic period (2925-2575 BCE), the Old Kingdom (2575-2130 BCE), the 1st Intermediate period (2130-2080 BCE), the Middle Kingdom (1938-1600 BCE), the 2nd Intermediate period (1630-1540 BCE), and the New Kingdom (1470-11 century BCE). During the first period, two kingdoms on both sides of the river Nile were united under the first pharaoh/king, the first step pyramid was constructed, and writing was invented. In the 2nd period, the pharaohs had complete power and many pyramids were built (with limestone) until they became low on money which caused unrest with the nobles who usurped the power of weak pharaohs. The 3rd period was anarchy. The 4th restored stability and power to the government. Egypt had strong influence in Palestine and south along the Nile. Public works replaced pyramid building. The 5th brought revolts by the nobles and weakened pharaohs power. About 1630 BCE the Hyksos conquered Egypt bringing horse drawn chariots and new weapons. The Egyptians revolted in the 18th dynasty, and in the 6th period, Egypt became a military power and expanded its kingdom eastward to Euphrates and in the Mediterranean region under pharaoh Thutmose III. The new monarchy restored temples and palaces. Art became more natural and realistic rather than stylized. During the 12th century, Egyptian power declined, and in 525 Persia invaded, in 332 the Greeks invaded and then Rome.
Egyptian art depicts more daily tasks and family life whereas Mesopotamian art is more ceremonial. Egyptians believe in life after death and taking objects with you to help your passage. Clear social structures existed for both civilizations with the nobility far above the rest, and slavery existed. They had a patriarchal family structure with one wife and possible concubines. Divorce was possible.
Important Dates and Events
1. 612 BCE-Chaldeans conquered Babylon. The Chaldeans brought their influence to Babylon with them. They constructed the hanging gardens which is one of the seven wonders of the world now, and they brought great astronomical knowledge as well as prosperity to the country. They were a religious people as well, mixing their religion with the Babylonians’.
2. 1630 BCE-Hyksos conquer Egypt, bringing horse drawn chariots and new weapons.
3. 332 BCE-Egypt is conquered by Alexander the Great, bringing Greek style of dress and cultural influence.
4. 2925-2575 BCE-1st pyramid is built, starting the legacy of Egyptian architecture and helping preserve their history.
5. 1000 BCE-Assyrians conquer Babylon, adding decoration and complexity to the Babylonian style of clothing and weaponry as well as introducing cotton to Assyria.
6. 1504-1450 BCE Thutmose III is pharaoh, making Egypt a military power, building/restoring temples and palaces. Art forms become more natural and realistic versus the earlier stylized version.
Significant Art and Architecture
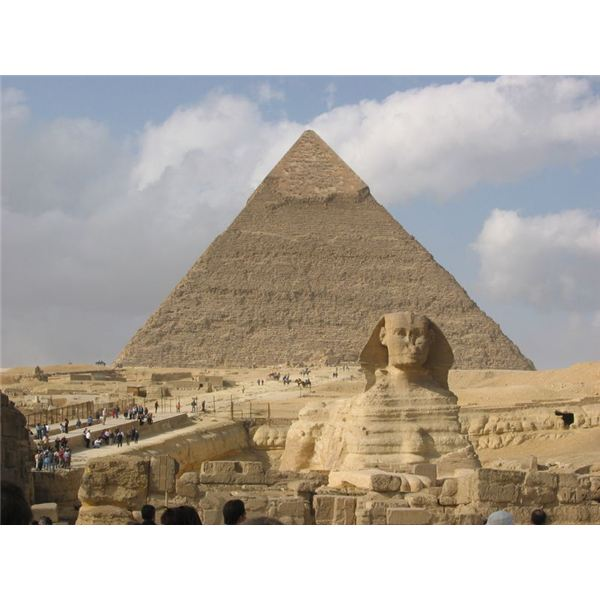

1.The Pyramid of Giza, Egypt.
Made by order of the pharaohs during the Old Kingdom. They were a symbol of wealth and power and were used as tombs for the royal family.
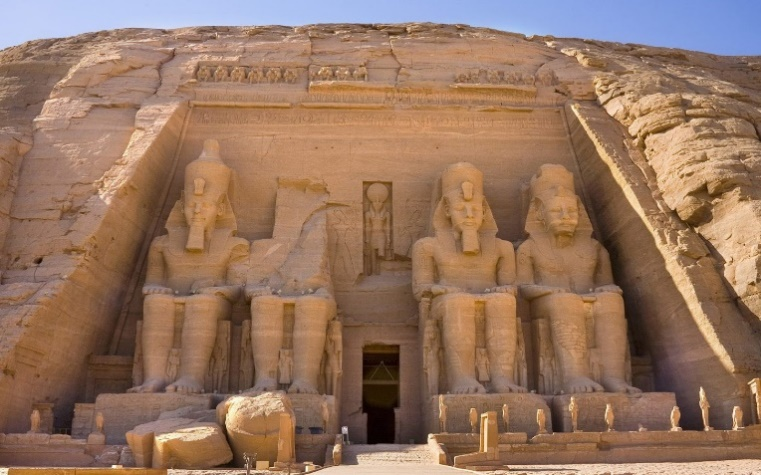

2.Temple of Abu-Simbel in Egypt. Built by Ramesses II during the 19th Dynasty of Egypt.

3. Example of wall painting and hieroglyphics.
Significant people
1. 1504-1450 BCE-Thutmose III, as pharaoh, made Egypt a military power, expanded their territory eastward, and built/restored temples and palaces. Art forms became more natural and realistic versus the earlier stylized version.
2. 1792-1750 BCE-King Hammurabi Extended control northward and created famous code of law which influenced later middle eastern law codes, including the law of Moses.
3. 356 -323 BCE-Alexander the Great was a Greek from Macedonia who extended the Greek empire significantly, conquered most of Europe and the middle east, and ended Persian rule in Egypt. He spread Greek culture wherever he went including the clothing that they wore.
4. 1350 BCE-King Tutankhamen’s tomb, excavated in the 1920s, having remained untouched for thousands of years, gave us valuable knowledge about Egypt during that time.
5. 700 BCE-Assyrian King Sennacherib introduced cotton to Assyria.
6. Around1500 BCE- Queen Hatshepsut was one of the few female pharaohs in Egypt and rulers of the ancient world.
Important Terms
- Kaunakes: fleece or fleece like fabric.
- Chignon: a bun of hair at the back of the neck held in place by a fillet.
- Fillet: a cloth or metal headband.
- Tunic: a t shaped garment with openings for the head and arms.
- Linen: cloth made from fiber removed from the stem of the flax plant.
- Flax: the term for linen before it is properly prepared for spinning.
- Mordant: a substance used to fix colors in fabric.
- Warp yarn: weaving consisting of interlacing lengthwise yarns.
- Weft/filling yarn: weaving with interlacing crosswise yarns.
- Selvage: the place on the side where the weft yarn returns to make its return trip across the fabric.
- Pectorals: decorative pendants or ornaments that hung down on the chest.
- Seams: places where one piece of cloth is joined to another.
- Sheath dress: closely fitted garment.
- Kalasiris: fringed tunic or sheath dress.
- Schenti: wrapped skirt.
- Amulet: charms worn around the neck to ward off evil.
- Diadems: crowns.
- Henna: a reddish hair dye possibly used to color nails.
- Kohl: a paint made from galena, a sulfide of lead.
- Lock of Youth/Horace: a shaved head with one lock of hair on the left side remaining.
Visual Examples
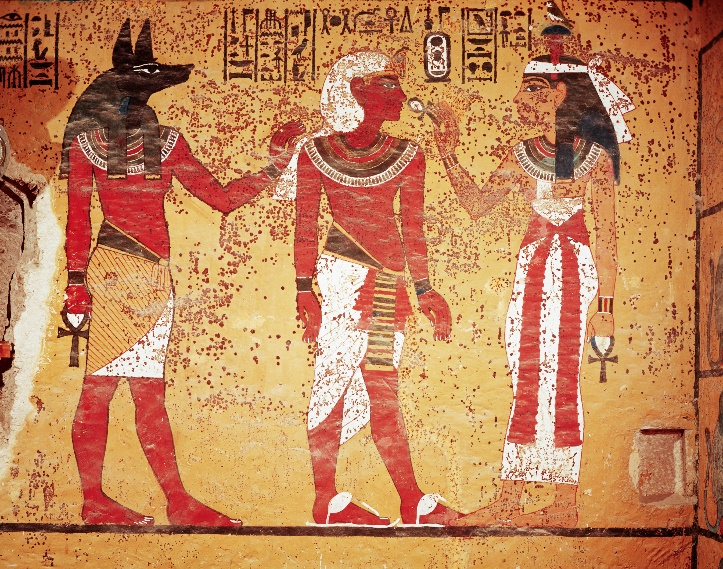


Left: Egyptian wall painting depcting King Tut with the Gods: Anubis and Nephthys. Right: Statue depicting Assyrian ruler.


Left: Egyptian wall painting depicting pharaoh at war. Right: Sumerian worshiper

-Major Mesopotamian and Egyptian Garments.

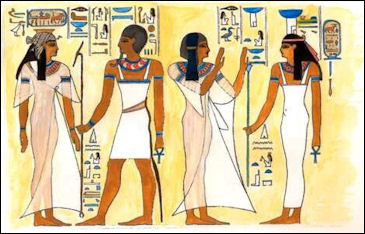
Left: Egyptian wall painting with pharaoh and Gods. Right: Wall painting of Queen Bint-Anath


Left: Women’s gold Headdress and jewelry–probably a royal women’s in Ur in Mesopotamia about 2800 BCE. Right: A recreation of what the Hanging Gardens of Chaldean Babylon might have looked like. Like most of the 7 wonders of the ancient world, they no longer exist today.


Left: Ancient Egypt pyramid/sphinx of Giza Right: Temple of Karnak
Thanks for reading!!!!! XOXO!


It would be interesting to learn more about what styles developed throughout the ages and why, what influences come into play, see the evolution of a culture’s fashion with explanations pointing out the details in the garment/style that showcase those influences/changes.
LikeLiked by 1 person